Journal entry to reissue treasury stock
Treasury Shares Accounted for at Par
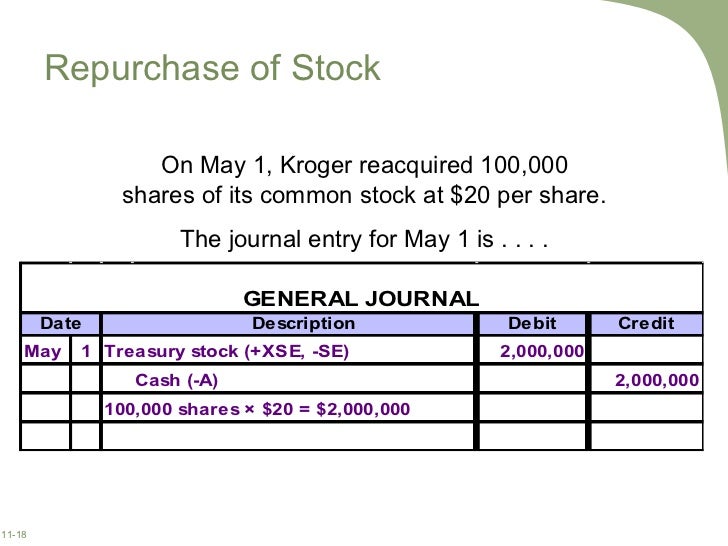
Cost method is one of the two methods of accounting for treasury stock, the stock which has been bought back by the issuing company itself. The other method is called the par value method. Under the cost method, the purchase of treasury stock is recorded by debiting treasury stock account by the actual cost of purchase.
The cost method ignores the par value of the shares and the amount received from investors when the shares were originally issued.
When treasury shares are later reissued, the treasury stock account is credited for the cost at which they were purchased, cash account is debited for the amount actually received and if the amount received on reissuance of treasury stock is:. Written by Irfanullah Jan.
Treasury Stock - Intermediate Accounting - Journal EntriesContact Us Privacy Policy Disclaimer. When treasury shares are later reissued, the treasury stock account is credited for the cost at which they were purchased, cash account is debited for profit and loss calculator forex amount actually received and if the amount received on reissuance of treasury stock is: The following example central ky livestock market the cost method of accounting for treasury stock: Pass journal entries to record the above transactions.
Solution Issuance of Common Stock: Cash 53, Common Stock 50, Additional Paid-In Capital 3, Purchase of Treasury Stock Cost Method: Treasury Stock 5, Cash 5, Journal entry to reissue treasury stock of Treasury Stock Cost Method: Cash 3, Treasury Stock 3, Additional Paid-In Capital Financial Accounting Financial Accounting Intro Accounting Principles Accounting Cycle Financial Statements Subsequent Events Cash and Cash Equivalents Receivables Inventories Other Current Assets Non-Current Assets Investments Revenue Recognition Employee Benefits Accounting for Taxes Lease Accounting Shareholders' Equity Current Liabilities Long-term Liabilities Partnership Accounting Business Combinations Financial Ratio Analysis Specialized Ratios Managerial Accounting Managerial Accounting Intro Cost Classifications Cost Accounting Systems Cost Allocation Cost Behavior Analysis Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis Relevant Costing Capital Budgeting Master Budget Inventory Management Standard Costing Performance Measurement Miscellaneous Time Value of Money Corporate Finance Forms of Business.
Current Chapter Shareholders' Equity Common Stock Preferred Stock Issuance of Shares Issuance of Shares: Non-Cash Lump-Sum Stock Issuance Treasury Stock Cost Method Treasury Stock Par Value Method Cash Dividends Stock Dividends Stock Splits Retained Earnings.